Skin conditions are a wide range of medical issues that impact the skin, the body’s largest organ. These disorders can vary greatly in severity and symptoms, impacting the skin’s appearance, texture, and overall health. Understanding the different types of skin disorders, their causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options is essential for effective management and care.
Types of Skin Disorders
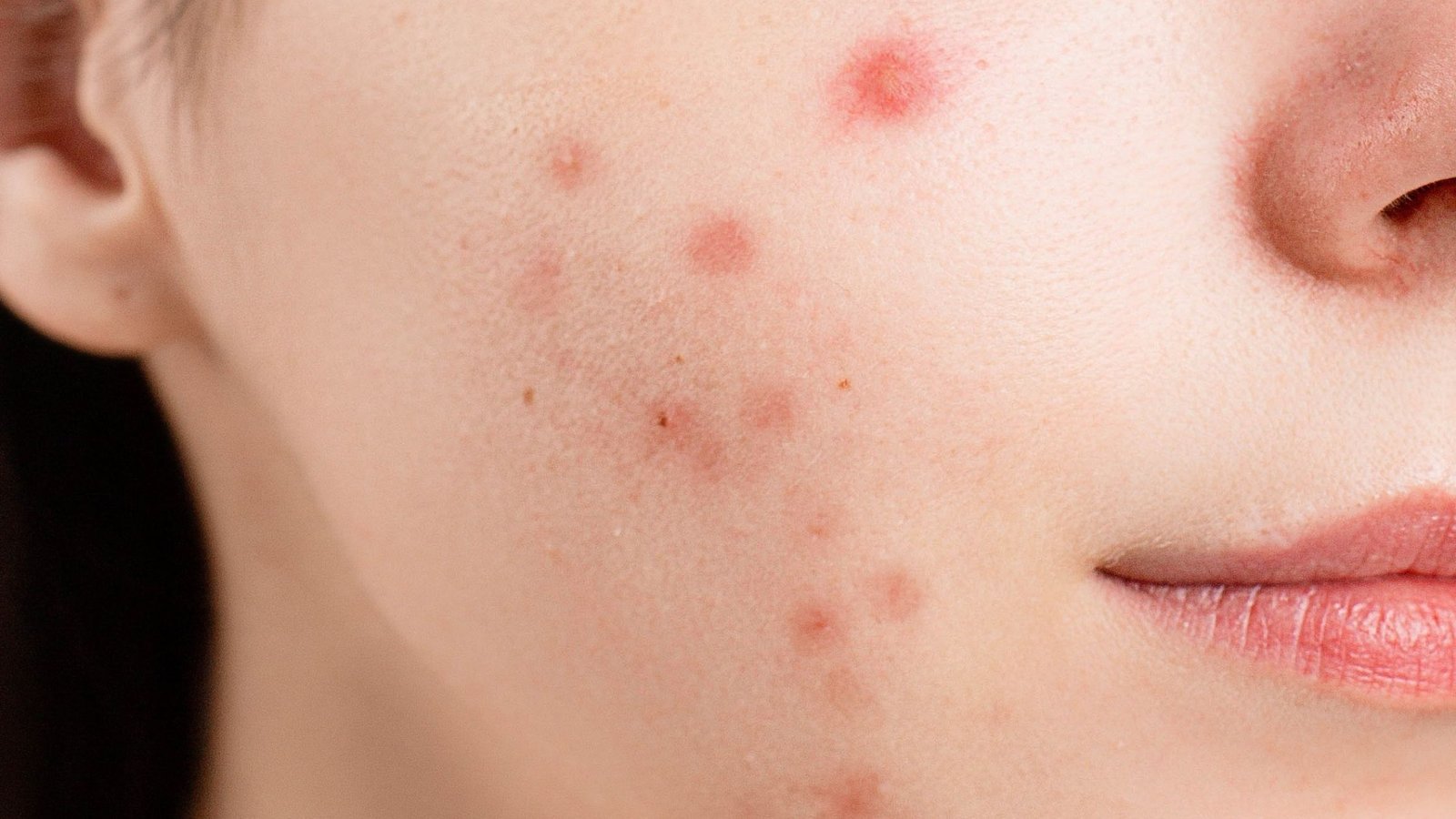
- Acne: Acne is one of the most common skin conditions, particularly affecting teenagers and young adults. It involves the clogging of hair follicles with oil and dead skin cells, leading to pimples, blackheads, and sometimes cysts.
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): Eczema is a chronic condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It often appears in childhood but can persist into adulthood.
- Psoriasis: Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder that causes the rapid buildup of skin cells, leading to thick, scaly patches. These patches are often red and itchy.
- Rosacea: Rosacea primarily affects the face, causing redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes red, pus-filled bumps.
- Dermatitis:
- Contact Dermatitis: Triggered by direct contact with allergens or irritants.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Affects oily areas of the body, such as the scalp, causing scaly patches and dandruff.
- Skin Infections:
- Bacterial: Includes conditions like impetigo, caused by bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus.
- Viral: Examples include herpes simplex (cold sores) and warts caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV).
- Fungal: Athlete’s foot and ringworm are common fungal infections.
- Parasitic: Scabies, caused by tiny mites that burrow into the skin.
- Skin Cancer:
- Basal Cell Carcinoma: The most common and least dangerous type.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: More aggressive than basal cell carcinoma but less common.
- Melanoma: The most serious type of skin cancer, known for its ability to spread to other parts of the body.
- Vitiligo: A condition characterized by the loss of pigment-producing cells in the skin, leading to white patches.
- Hives (Urticaria): Raised, itchy welts that can appear suddenly due to allergic reactions or other triggers.
Causes of Skin Disorders
Skin disorders can result from a variety of factors, including:
- Genetics: Many conditions, such as eczema and psoriasis, have a genetic component.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to pollutants, allergens, and irritants can trigger or worsen skin conditions.
- Immune System Issues: Autoimmune disorders like psoriasis occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells.
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, fungal, and parasitic infections can lead to skin problems.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can affect the skin.
- Lifestyle Factors: Diet, stress, and personal hygiene practices significantly impact skin health.
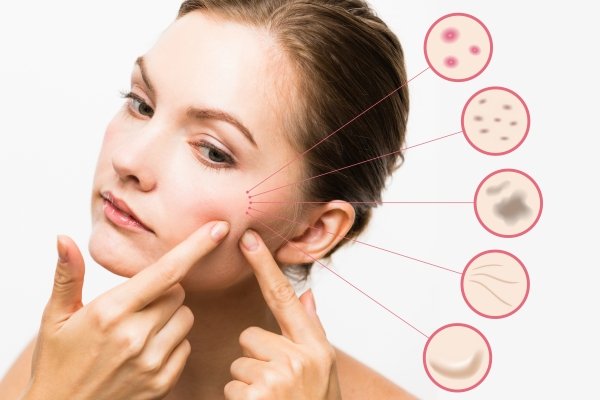

Symptoms of Skin Disorders
Symptoms vary widely depending on the specific disorder but can include:
- Redness and Inflammation: Common in conditions like eczema, rosacea, and dermatitis.
- Itching: A frequent symptom in many skin conditions, including eczema and hives.
- Dryness and Scaling: Often seen in psoriasis and eczema.
- Blisters and Pustules: Present in acne, impetigo, and herpes infections.
- Pigment Changes: Occur in conditions like vitiligo and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Pain: Some conditions, particularly infections and severe acne, can cause pain.
Diagnosis of Skin Disorders
Diagnosing skin disorders typically involves:
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination of the skin by a dermatologist.
- Medical History: Reviewing the patient’s symptoms, family history, lifestyle factors, and potential triggers.
- Skin Biopsy: Removing a small sample of skin for laboratory analysis to confirm the diagnosis.
- Allergy Tests: Identifying specific allergens that may be causing or exacerbating the condition.
- Blood Tests: Checking for underlying conditions or autoimmune markers.
Treatment of Skin Disorders
Treatment options vary depending on the specific disorder and may include:
- Topical Treatments: Creams and ointments containing steroids, antibiotics, or other active ingredients to reduce inflammation and treat infections.
- Oral Medications: Antibiotics, antihistamines, or immune-modulating drugs for more severe cases.
- Light Therapy: Using ultraviolet light to treat conditions like psoriasis and eczema.
- Lifestyle Changes: Modifying diet, managing stress, and maintaining a proper skincare routine.
- Surgery: For severe cases of skin cancer or to remove persistent cysts and lesions.
- Alternative Therapies: Herbal treatments, acupuncture, and other holistic approaches, though these should be used with caution and under medical advice.
Prevention of Skin Disorders
Preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing skin disorders:
- Good Hygiene Practices: Regular cleansing to remove dirt and bacteria.
- Moisturizing: Keeping skin hydrated to prevent dryness and irritation.
- Sun Protection: Using sunscreen to prevent sunburn and reduce the risk of skin cancer.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding known allergens and irritants.
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals that support skin health.
- Regular Dermatological Check-Ups: Early detection and management of potential skin issues.
Conclusion
Skin disorders encompass a wide range of conditions that can significantly impact an individual’s health and well-being. Understanding the types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for effective management. If you suspect you have a skin disorder, it is important to seek professional medical advice for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. With proper care and management, many skin conditions can be effectively controlled, leading to improved skin health and quality of life.